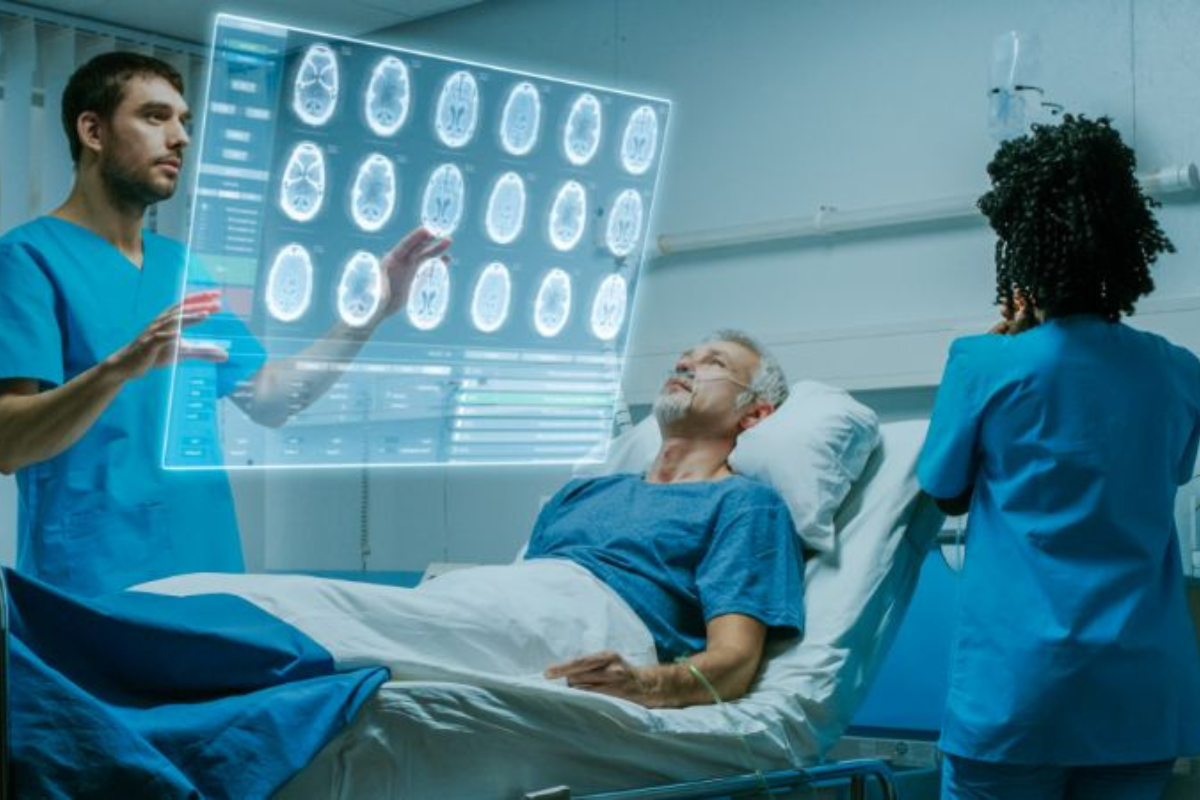
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are immersive technologies that can revolutionize the healthcare sector by improving the quality of care for patients, training medical professionals, and streamlining surgical procedures. According to reports, the global AR healthcare market was valued at $609.60 million in 2018 and is projected to reach $4,237.60 million by 2026, indicating that AR technology is here to stay.
One significant benefit of AR in healthcare is the training of medical professionals. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AR played a critical role in developing the skills of medical students. For instance, Barts Health NHS Trust and the Queen Mary University of London introduced virtual ward rounds for students. Professor Shafi Ahmed wore a Microsoft Hololens headset during his ward rounds, which was livestreamed to students in a lecture theatre. This approach allowed students to see patients through the professor’s eyes and access in-depth patient medical records, including X-rays and CT scans, as well as patient consultations and examinations.
AR can also assist surgeons during surgical procedures by accessing critical real-time patient data, including heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, and breathing rate. The first-ever AR guided operation was performed at the Sant’Orsola hospital in Bologna in February 2020. Giovanni Badiali, the lead surgeon, used an AR headset to access real-time patient data during the procedure.
In addition, AR technology has been adopted by nurses and doctors to improve vein detection. AR-driven technologies such as Accuvein can be applied to detect veins more effectively and provide guidance for undertaking intravenous injections with minimal discomfort for the patient.
AR technology can enhance patient consultations, allowing patients to gain more in-depth and informed insights into their medical conditions. For instance, AR can enable patients to see what someone with macular degeneration sees or to view a disease or condition on their own skin.
AR can also build on established technologies such as X-rays and CT scans. By creating 3D models of a patient’s body, AR can provide medical professionals with a more accurate and detailed view of a patient’s condition, allowing for better diagnosis and treatment.
Takeaway
It is evident that the potential of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in the healthcare sector is immense. The advancements in these technologies have opened up new opportunities for medical professionals to provide more efficient and personalized care to their patients, while also enabling better training and education for medical students.
The use of AR and VR can enhance patient outcomes by improving diagnosis accuracy, treatment effectiveness, and post-operative care. For instance, these technologies can help doctors to visualize and plan complex surgical procedures, thereby reducing the risk of errors and improving patient safety. Additionally, VR-based therapy can be used to treat mental health conditions, such as anxiety and PTSD, by creating immersive and controlled environments for patients to confront their fears.
Furthermore, AR and VR can also transform the way medical professionals are trained. Medical students can use these technologies to simulate surgical procedures, practice diagnosis, and learn about the human body in a more interactive and engaging way. This can help to reduce the costs and risks associated with traditional training methods, while also ensuring that medical professionals are better prepared for real-life scenarios.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential of AR and VR in the healthcare sector will only continue to grow. With the ability to streamline surgical procedures, enhance medical training, and improve patient outcomes, it is clear that AR and VR will play a significant role in shaping the future of healthcare. By embracing these technologies, medical professionals can provide better care to patients and create a more efficient and effective healthcare system for all.